Click New Line to get a new default rule. Leave this unchanged. The default rule that you begin with denies everyone everything. Once you've done this, you can expand the access to include specified users and groups, as in the next step.
Click New Line again to get another default ACL rule as the bottom row of the table. You can use the up and down arrows in the left column to move a rule, if needed.
Figure 7.2 A sample ACL for the owner of a file
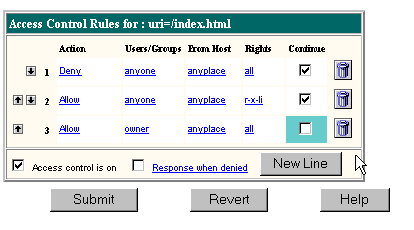
You can allow access to this file by clicking the Deny link in the Action column. The bottom frame now displays the Allow/Deny form. See the section See "Setting Actions" for more details.
Click Allow and then click Update to return to the top frame with the new data.
You can allow access to a specific user by clicking the Anyone link in the Users/Groups column. The bottom frame now displays the User/Group form. By default, there is no authentication, meaning anyone can access the resource. See "Setting Users and Groups" for more details.
You can restrict access to a computer or network by clicking the Anyplace link in the From Host column. See "Specifying Host Names and IP Addresses" for more details on how to use this advanced option.
You can restrict access to certain operations by clicking the All link in the Rights column. The bottom frame now displays the Access Rights form. By default, the user has access to all operations. See "Setting Rights" for more details.
Add another new line, this time allowing the owner to have write and delete access as well. Complete steps 4-6.
In most cases, this is all you need to do to define an ACL for your file, so click Submit to set up this ACL for your index.html file. See "Additional Options" for details about other options you can use.